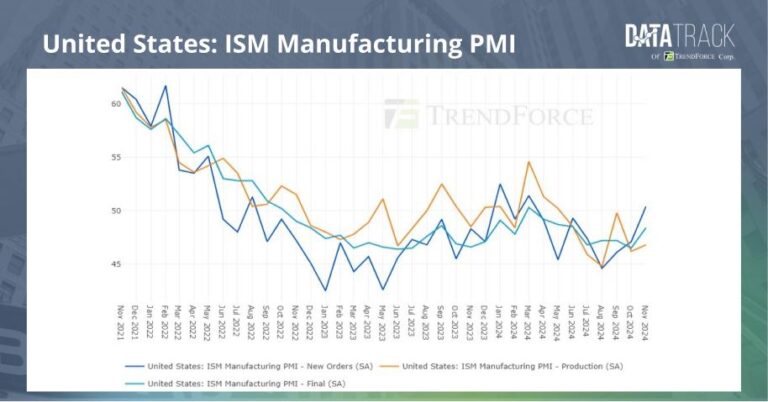
Persistent Decline in US Manufacturing Amid Escalating Tariff Challenges
The US manufacturing industry has experienced a notable downturn, marking its sixth straight month of contraction as of April. This sustained slump reflects the mounting difficulties manufacturers face due to ongoing tariff impositions and supply chain interruptions. Diminished export demand and restrained capital expenditures have considerably dampened production levels, signaling a broader cooling trend in industrial output across the nation. Experts largely attribute this decline to the trade frictions that have increased operational costs and disrupted long-standing supply arrangements.
Recent manufacturing metrics highlight several critical trends:
- New order volumes continue to fall, indicating weak international demand.
- Factory employment has softened as businesses navigate uncertainty.
- Supplier lead times have lengthened, complicating production scheduling and inventory control.
Considering these challenges, many companies are adopting conservative inventory management and postponing capital investments until trade policies become more predictable. The persistence of these obstacles raises alarms about potential spillover effects on the wider economy if manufacturing conditions fail to rebound soon.
Tariff Effects on Supply Chains and Global Competitiveness
US manufacturers continue to face meaningful disruptions stemming from prolonged tariff enforcement, which has unsettled established supply chain frameworks and driven up production expenses. These tariffs have compelled firms to rethink their sourcing strategies, often leading to delayed shipments and higher inventory holding costs. Such disruptions not only reduce operational efficiency but also hinder manufacturers’ agility in responding to shifting market demands.
Several key factors exacerbate these challenges:
- Shifting procurement to more expensive suppliers outside preferred trade agreements.
- Increased administrative complexity due to stringent customs and compliance protocols.
- Declining export competitiveness as rising input costs inflate final product prices in global markets.
| Area of Impact | Consequence | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain Delays | Lead times extended by up to 20% | Over 6 months |
| Cost Inflation | Input prices increased by 5-12% | Ongoing |
| Export Volumes | Year-over-year decline of 8% | Past 6 months |
Domestic Employment and Industry Growth Under Pressure
The ongoing contraction in manufacturing has had tangible effects on employment within the sector, with layoffs and hiring slowdowns becoming increasingly common in industrial hubs across the US. Elevated input costs driven by tariffs have forced many manufacturers to curtail workforce expansion or reduce staff to manage expenses. This trend has contributed to rising unemployment rates in regions heavily reliant on manufacturing jobs, fueling concerns about job security among skilled workers and technicians. Additionally, the shift toward automation and offshoring is intensifying uncertainty for traditional blue-collar roles.
Growth prospects for the industry have also dimmed, as companies delay or cancel expansion initiatives amid unpredictable trade policies and rising production costs. Key sectors such as automotive and consumer electronics report significant cutbacks in capital spending and research activities. These effects ripple through supply chains,placing pressure on domestic suppliers and threatening the sustainability of US-based manufacturing operations. Industry leaders stress the urgent need for policy reforms to stimulate innovation, investment, and job creation.
- Employment Trends: Manufacturing jobs have decreased by 4.6% since the last fiscal quarter.
- Capital Expenditure: Forecasted to decline by 12% over the next two years.
- Automation Uptake: Increased by 8% as firms seek operational efficiencies.
| Industry Segment | Job Loss (%) | Investment Change (%) | Growth Outlook |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 5.1 | -15 | Stagnant to Negative |
| Consumer Electronics | 3.8 | -10 | Declining |
| Textile Manufacturing | 4.4 | -8 | Marginal Growth |
Strategic Policy Initiatives to Counteract Tariff Impacts and Stimulate Manufacturing
To reverse the persistent downturn in manufacturing exacerbated by tariff-related cost pressures, policymakers must implement targeted approaches that balance protective trade measures with the need for competitiveness. Scaling back excessive tariffs on essential raw materials and intermediate goods can ease cost burdens, helping manufacturers sustain profitability and preserve employment. Concurrently, enhancing trade agreements to diversify sourcing and export destinations will reduce dependency on vulnerable markets affected by tariffs.
Moreover, investing in innovation and workforce development is critical to revitalizing the US manufacturing landscape. Initiatives aimed at upskilling workers in automation and advanced manufacturing technologies will enhance productivity and global market positioning. Industry experts recommend the following policy actions:
- Gradual elimination of non-essential tariffs to lower production expenses
- Expansion of export support programs to access emerging markets
- Incentives promoting adoption of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing technologies
- Public-private collaborations focused on retraining displaced manufacturing employees
| Policy Focus | Recommended Measures | Anticipated Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Tariff Adjustment | Lower tariffs on critical inputs | Reduced manufacturing costs |
| Innovation Support | Tax incentives for tech investments | Enhanced productivity and competitiveness |
| Workforce Enhancement | Funding for reskilling and training programs | Greater labor market versatility |
Conclusion: Manufacturing Outlook and Policy Pathways Forward
As US manufacturing contracts for a sixth month in a row, the sector’s challenges—driven largely by sustained tariff pressures and global trade uncertainties—remain a focal point for economists and industry stakeholders. This prolonged decline highlights the urgent need for strategic policy interventions to support the industry’s recovery and long-term vitality.Moving forward, a balanced approach that reduces tariff burdens, fosters innovation, and invests in workforce development will be essential to restoring growth and competitiveness in American manufacturing.