Rising Police Budgets Amidst Calls to Defund: A Closer Look at U.S. Cities
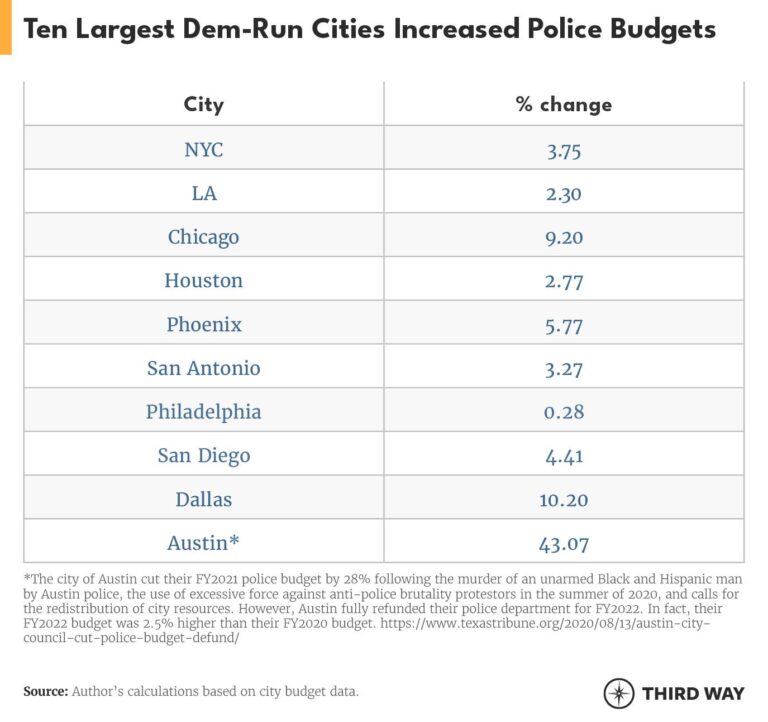
Despite the widespread advocacy to “defund the police,” many prominent American cities have paradoxically increased their law enforcement budgets in recent years. City officials frequently enough justify these hikes by pointing to escalating crime rates, population growth, and the necessity for improved training and modern equipment. As an example, metropolitan areas such as Chicago, Los Angeles, and Houston have approved police budget increases ranging from 5% to 12%, highlighting the tension between reformist demands and public safety priorities.
Several key elements contribute to this upward trend in police funding:
- Enhanced support for community policing programs designed to build stronger neighborhood relationships.
- Investment in cutting-edge technology, including body-worn cameras and advanced data analytics tools.
- Expanded mental health and crisis response training aimed at minimizing violent confrontations.
- Efforts to counteract the surge in violent and property crimes observed during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
| City | Increase in Police Budget | Main Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Chicago, IL | 8% | Crime Increase & Equipment Modernization |
| Los Angeles, CA | 6.5% | Expansion of Community Policing |
| Houston, TX | 7.2% | Crisis Intervention Training |
| New York City, NY | 5% | Technology and Data System Upgrades |
Evaluating the Effects of Increased Police Spending on Public Safety Outcomes
While many cities have boosted police budgets, the relationship between these increases and improvements in community safety is multifaceted. Some urban areas report reductions or stabilization in violent crime rates, whereas others continue to face persistent safety challenges despite higher expenditures.
Factors that influence how effectively increased funding translates into safer communities include:
- Targeted officer training focused on de-escalation techniques and cultural awareness.
- Collaborative efforts integrating social workers and mental health experts alongside police officers.
- Community engagement initiatives that build trust and encourage cooperation between residents and law enforcement.
- Robust transparency and accountability frameworks to monitor police conduct and spending.
| City | Police Budget Change (2019-2023) | Change in Homicide Rate (%) | Number of Funded Community Safety Programs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chicago | +12% | -5% | 5 |
| Los Angeles | +8% | +2% | 3 |
| New York City | +10% | -7% | 6 |
| Seattle | +4% | +10% | 4 |
Underlying Causes Behind the Expansion of Law Enforcement Budgets
Across the nation, city governments are under increasing pressure to enhance public safety amid concerns about rising violent crime and social unrest. Many officials argue that augmenting police funding is critical to effectively tackling these issues. The primary factors fueling this budget growth include:
- Deployment of sophisticated surveillance and communication technologies to improve emergency response and investigations.
- Efforts to recruit and retain officers in the face of high retirement rates and workforce attrition.
- Support for specialized divisions addressing cybercrime, narcotics, and mental health emergencies.
- Expansion of community policing to rebuild public trust and proactively prevent criminal activity.
These priorities frequently enough take precedence over budget reduction initiatives, as cities navigate the delicate balance between fiscal duty and public safety demands. The following table highlights recent budget changes in select metropolitan areas:
| City | 2022 Police Budget | 2023 Police Budget | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chicago | $1.8 Billion | $2.0 Billion | +11% |
| New York City | $5.5 Billion | $5.8 Billion | +5% |
| Los Angeles | $1.7 Billion | $1.9 Billion | +12% |
| Seattle | $400 Million | $420 Million | +5% |
Strategies for Harmonizing Public Safety with Community Investment
To effectively address the nuanced challenges revealed by recent police budget increases, municipalities must adopt comprehensive approaches that emphasize both accountability and community empowerment. Recommended strategies include:
- Open budget transparency: Cities should facilitate public discussions that critically assess police spending alongside investments in community programs to promote fiscal accountability.
- Broadened support for community services: Allocating resources to mental health care, affordable housing, and youth development can alleviate reliance on traditional policing and foster safer environments.
- Advanced officer education: Prioritizing training in conflict resolution, cultural sensitivity, and crisis management can enhance public trust and improve outcomes during police encounters.
Below is a proposed budget distribution model that balances law enforcement needs with community development priorities:
| Category | Budget Allocation (%) |
|---|---|
| Police Operations and Training | 45% |
| Community Outreach and Programs | 30% |
| Mental Health and Crisis Response | 15% |
| Housing and Social Support Services | 10% |
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex Landscape of Police Funding and Reform
As discussions surrounding policing and public safety continue to evolve across the United States, a clear gap remains between activist rhetoric and fiscal realities. Despite vocal demands to reduce police budgets, data from numerous cities—including Chicago—indicates that law enforcement funding has, in fact, grown. This divergence highlights the intricate challenges faced by policymakers and communities striving to reconcile calls for reform with the imperative to maintain public security. Moving forward, a nuanced understanding of budget allocations and their impacts will be crucial in shaping effective and equitable policing strategies nationwide.