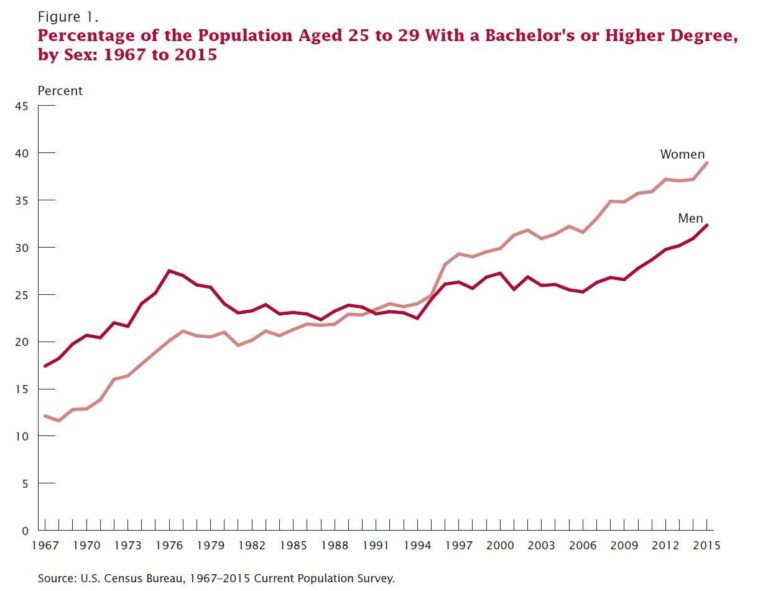
U.S. Women Lead Men in College Graduation Rates Across All Major Racial and Ethnic Groups
A recent analysis by the Pew Research Center uncovers a notable evolution in higher education: women in the United States are now graduating from college at higher rates than men across every significant racial and ethnic category. This widespread trend transcends demographic boundaries, signaling a fundamental shift in educational achievement patterns and hinting at far-reaching socioeconomic consequences. The data illuminate changing gender dynamics within American academia and suggest new trajectories for workforce composition and economic empowerment.
College Completion Rates: Women Outperform Men Across Diverse Communities
According to the latest Pew Research findings, women consistently surpass men in earning college degrees among White, Black, Hispanic, and Asian American populations. This pervasive pattern reflects a broader societal change in educational priorities and gender roles. The gains made by women are particularly striking among Black and Hispanic groups, where the gap has widened most substantially.
- Women’s college graduation rates exceed men’s by margins ranging from 5% to 15% across all racial and ethnic groups.
- Black and Hispanic women have experienced the most ample improvements relative to their male peers.
- These trends coincide with increased female participation in traditionally male-dominated academic disciplines.
| Racial/Ethnic Group | Women’s Graduation Rate | Men’s Graduation Rate | Gap |
|---|---|---|---|
| White | 63% | 53% | +10% |
| Black | 57% | 44% | +13% |
| Hispanic | 52% | 42% | +10% |
| Asian American | 73% | 61% | +12% |
Key Drivers Behind the Expanding Gender Gap in Higher Education
The widening disparity in college completion rates between women and men stems from a combination of social, academic, and economic factors. From early childhood, girls tend to excel in literacy and dialog skills, which lays a strong foundation for academic success throughout their educational journey. Additionally, cultural shifts that emphasize women’s career advancement, coupled with increased institutional support such as mentorship programs, have empowered more female students to persist and graduate.
Economic considerations also play a crucial role. Women frequently enough perceive greater long-term benefits from higher education, including enhanced career prospects and financial independence, which motivates sustained enrollment and degree completion.Meanwhile, men may face societal pressures to enter the workforce earlier, impacting their educational trajectories.
- Academic Preparedness: Girls generally show higher engagement in language arts and social sciences during K-12 education.
- Institutional Resources: Universities have expanded mentorship and networking opportunities tailored to female students.
- Labour Market Incentives: Women’s employment outcomes are more strongly linked to educational attainment.
- Societal Norms: Evolving gender roles encourage women to pursue higher education as a path to empowerment.
| Factor | Effect on Women | Effect on Men |
|---|---|---|
| Early Academic Performance | Stronger focus and success in reading and writing | Lower engagement, particularly in literacy subjects |
| Support Systems | Access to targeted mentorship and support networks | Fewer tailored resources available |
| Social Expectations | Encouraged to pursue higher education | Frequently enough expected to join the workforce sooner |
| Economic Motivators | Strong link between education and career advancement | Less direct correlation observed |
Workforce Diversity and Economic Empowerment: The Broader Impact
The increasing prevalence of women earning college degrees is reshaping the American workforce, fostering greater diversity and inclusion across industries. Organizations are recognizing the competitive advantage of diverse teams, which often drive innovation and improved problem-solving. Women of color, in particular, are emerging as a vital talent pool, challenging historical underrepresentation in many professional sectors.
Educational attainment among women correlates strongly with economic empowerment,leading to higher earnings,increased financial autonomy,and more leadership opportunities. The following table highlights projected growth in sectors where women’s rising college completion rates are expected to influence workforce demographics:
| Industry Sector | Projected Workforce Growth (%) | Current Female Portrayal (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) | 15 | 28 |
| Healthcare | 20 | 75 |
| Education | 10 | 65 |
| Business and Finance | 12 | 48 |
Beyond workforce numbers, the rise in women’s educational attainment contributes to narrowing the gender wage gap and reducing economic disparities among racial and ethnic groups. Sustaining these positive trends will require continued investment in policies and programs that support women’s academic and professional advancement, ensuring that increased diversity translates into equitable economic outcomes.
Strategies to Enhance Male College Completion and Foster Educational Equity
To address the persistent gender gap in college graduation rates, it is indeed essential to implement targeted interventions that support male students, particularly those from underrepresented racial and ethnic backgrounds. Expanding mentorship programs tailored to men,increasing financial aid opportunities,and offering flexible learning options can significantly improve male student retention and success.
Early engagement initiatives in high schools that encourage male students to pursue higher education are also critical. Collaborative efforts among policymakers, educators, and community organizations can create supportive environments that address the unique challenges faced by male students.
- Enhanced Academic Advising: Provide male-focused guidance on course selection and career pathways.
- Mental Health Support: Develop counseling services attuned to the specific needs of male students.
- Community Building: Foster male peer networks and leadership opportunities to boost engagement.
| Policy Focus | Recommended Initiative | Anticipated Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Assistance | Expand scholarships targeting male students | Lower dropout rates linked to financial hardship |
| Mentorship Programs | Establish male mentorship networks | Boost academic motivation and retention |
| Mental Health Services | Implement tailored counseling initiatives | Improve well-being and reduce attrition |
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Gender and Education in America
The trend of U.S. women outpacing men in college completion across all major racial and ethnic groups marks a pivotal transformation in the educational landscape. This shift not only reflects changing societal norms and academic engagement but also carries significant implications for workforce diversity, economic equity, and social mobility. Understanding and addressing the underlying causes of this gender gap will be vital for educators, policymakers, and communities striving to create an inclusive and equitable higher education system that benefits all students.