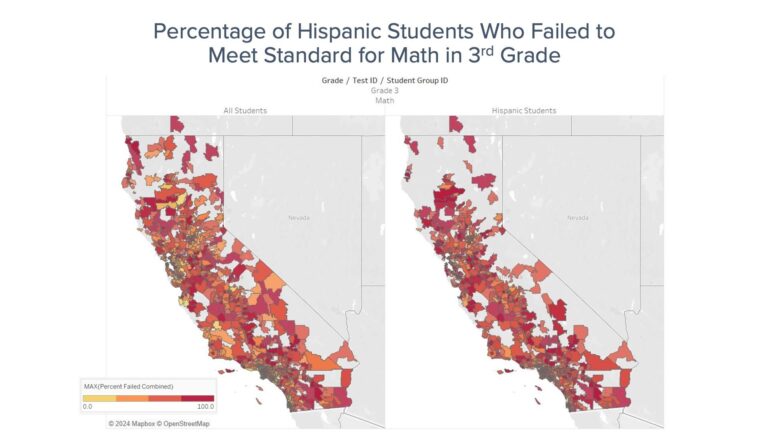
Rising Educational Disparities Between Latino and White Students
Recent analyses reveal an alarming increase in the educational achievement gap separating Latino students from their white counterparts. Despite ongoing national initiatives aimed at promoting equity, key academic indicators such as graduation rates, standardized test outcomes, and college matriculation rates demonstrate a growing chasm. This trend poses significant risks to the socioeconomic advancement of Latino communities.Contributing factors include disparities in access to experienced educators, limited availability of advanced coursework, and socioeconomic hardships disproportionately affecting Latino families.
Several systemic barriers continue to sustain this divide:
- Chronic underfunding of schools predominantly serving Latino populations
- Insufficient bilingual education programs and lack of culturally inclusive curricula
- Elevated absenteeism rates linked to economic instability
- Restricted access to early childhood education opportunities
To effectively bridge this gap, comprehensive policy reforms and enhanced community engagement are essential to guarantee equitable educational experiences for all students.
| Indicator | White Students | Latino Students | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| High School Graduation Rate | 89% | 74% | 15 |
| College Enrollment Rate | 68% | 49% | 19 |
| Math Proficiency (8th Grade) | 48% | 29% | 19 |
Socioeconomic Influences and Resource Inequities Impacting Academic Achievement
Economic disparities remain a basic driver behind the educational achievement gap between Latino and white students. Latino communities frequently encounter limited access to high-quality instructional materials, under-resourced schools, and fewer opportunities for advanced academic programs. Schools with predominantly Latino enrollment often struggle with shortages of veteran educators and extracurricular activities that foster holistic development. These challenges contribute to diminished academic outcomes and hinder college preparedness, perpetuating cycles of disadvantage.
Key contributors to the expanding educational divide include:
- Latino families experience poverty at nearly twice the rate of white families
- Lower enrollment in early childhood education programs
- Fewer well-funded public schools located in Latino-majority neighborhoods
- Limited home access to technology and reliable high-speed internet
| Resource Category | White Students | Latino Students |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Advanced Placement Courses | 75% | 40% |
| Access to High-Speed Internet | 90% | 60% |
| Student-to-Qualified Teacher Ratio | 15:1 | 25:1 |
| Participation in After-School Activities | 50% | 28% |
Strategic Policy Solutions to Enhance Educational Equity
Educational leaders and advocates emphasize the necessity for deliberate policy measures that directly address the growing disparities in educational access and quality affecting Latino students. Central to these efforts is the call for increased investment in schools serving Latino communities, alongside the development of curricula that honor and incorporate students’ cultural identities.
Recommended strategies include:
- Expanding bilingual education initiatives to support language development while maintaining academic standards.
- Enhancing teacher professional development focused on cultural responsiveness and effective engagement with Latino learners.
- Establishing community mentorship programs to improve student retention and academic success.
- Reforming school funding formulas to ensure equitable resource distribution.
Recent data analyses demonstrate the positive impact of targeted funding and programmatic interventions on Latino student outcomes,underscoring the urgency for policy reform:
| Policy Initiative | Effect on Latino Student Achievement |
|---|---|
| Increased School Funding | 15% Improvement in Test Scores |
| Expansion of Bilingual Education | 12% Rise in Graduation Rates |
| Teacher Cultural Competency Training | 10% Boost in Student Engagement |
Community-Driven and School-Based Efforts to Narrow the Achievement Gap
In light of the persistent educational disparities,numerous grassroots organizations and educational institutions have initiated programs designed to reduce the achievement gap between Latino and white students.These efforts include mentorship programs, culturally relevant teacher training, and after-school STEM clubs that engage Latino youth through experiential learning. Emphasizing family engagement, bilingual instruction, and technology accessibility, these initiatives address the complex factors contributing to educational inequities.
Additionally, several school districts employ data-informed strategies to allocate resources effectively, focusing on early interventions and expanded support for English Language Learners (ELL). Below is an overview of prominent community and school-led programs currently in operation:
- Family Engagement Workshops: Strengthening partnerships between homes and schools.
- After-School Tutoring: Targeted assistance in literacy and mathematics.
- Culturally Responsive Curriculum: Incorporating students’ heritage to enhance motivation.
- Technology Access Initiatives: Providing devices and internet connectivity to underserved students.
| Program | Objective | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Bilingual Family Nights | Enhance parental involvement | Latino families |
| STEM Saturdays | Foster interest in STEM fields | Middle school students |
| ELL Support Circles | Improve English language skills | English Language Learners |
Final Thoughts on Bridging the Educational Divide
The expanding educational gap between Latino and white students, as illuminated by recent research, highlights enduring challenges within the American education system. To foster equitable opportunities, it is imperative that policymakers, educators, and communities address the underlying causes of these disparities. Prioritizing equitable resource distribution, culturally responsive teaching, and robust community partnerships will be crucial in closing the divide and promoting academic success for all students across diverse backgrounds.